Industries
Industries
As concerns about climate change intensify, industries across the globe are recognizing the imperative to reduce their carbon footprints.
In this overview, we explore the necessities and approaches to carbon reduction in key sectors, including Textile and Fashion, Manufacturing in the Automotive Industry, Logistics and Transportation, Construction, Real Estate, and Metal Products. By understanding the unique challenges and opportunities within each industry, we can foster a collective commitment to sustainable practices.
Textile and Fashion Industry

Necessities:
Resource Efficiency
Addressing excessive resource consumption, such as water and energy, throughout the production process.
Supply Chain Transparency
Comprehensively understanding the supply chain (from raw material extraction to manufacturing and distribution) to identify areas of improvement.
Approaches:
Circular Fashion
Adopting circular economy principles by promoting recycling, upcycling, and sustainable sourcing.
Eco-Friendly Materials
Utilizing alternative materials, such as organic cotton, bamboo, and recycled fibers, to reduce environmental impact.
Technology Integration
Implementing innovative technologies for energy-efficient production and waste reduction.
Manufacturing in the Automotive Industry
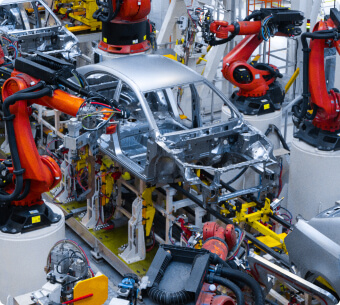
Necessities:
Emission Reduction
Tackling the carbon emissions associated with manufacturing processes, particularly in welding, painting, and assembly.
Supply Chain Optimization
Addressing emissions across the entire supply chain, including raw material extraction, component manufacturing, and assembly.
CBAM reporting
Submitting carbon footprint reports for imported goods under the CBAM directive.
Approaches:
Electrification
Shifting towards electric vehicle production to reduce dependence on fossil fuels.
Lightweight Materials
Incorporating lightweight materials to enhance fuel efficiency and reduce emissions.
Renewable Energy Integration
Embracing renewable energy sources for manufacturing facilities.
Logistics and Transportation

Necessities:
Fuel Efficiency
Enhancing the fuel efficiency of vehicles, airplanes, and ships to reduce emissions during transportation.
Smart Route Planning
Utilizing technology to optimize transportation routes and minimize fuel consumption.
Approaches:
Alternative Fuels
Exploring and adopting alternative fuels, such as biofuels and hydrogen, to mitigate the environmental impact.
Electric Fleets
Transitioning to electric vehicles for last-mile deliveries and urban logistics.
Collaborative Efforts
Collaborating with suppliers and partners to collectively reduce the carbon footprint of the entire supply chain.
Construction

Necessities:
Energy-Efficient Design
Incorporating energy-efficient design principles to reduce the energy consumption of buildings.
Waste Minimization
Implementing strategies to minimize construction and demolition waste.
Resilient Infrastructure
Building structures that can withstand the impacts of climate change.
Approaches:
Green Building Certifications
Pursuing and achieving certifications such as LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design).
Smart Technologies
Utilizing smart technologies for energy management, heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems.
Sustainable Materials
Opting for sustainable and recycled materials in construction projects.
Real Estate

Necessities:
Energy-Efficient Operations
Managing and optimizing energy consumption in buildings throughout their lifecycle.
CO2 footprint for M2 and benchmarking
Emissions-neutral operation
Achieving net-zero for buildings
Approaches:
Green Building Standards
Adhering to green building standards and certifications to ensure sustainability.
Renewable Energy Integration
Incorporating renewable energy sources, such as solar panels and wind turbines, into real estate developments.
Smart Building Solutions
Implementing smart technologies for energy monitoring, lighting, and waste management.
Metal Products

Necessities:
Energy-Efficient Manufacturing
Adopting energy-efficient practices in metal extraction, processing, and fabrication.
Recycling
Promoting the recycling and reuse of metal products to minimize the environmental impact.
Greener Products
Products with reduced GHG emissions.
Reporting to customers, investors and stakeholders
Submitting GHG emissions reports upon requests to ensure transparency.
Approaches:
Closed-Loop Systems
Implementing closed-loop systems that promote the circular economy for metals.
Lean Manufacturing
Adopting lean manufacturing principles to optimize processes and reduce waste.
Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS)
Exploring CCS technologies to capture and store carbon emissions produced during metal manufacturing.
By embracing sustainable practices in these industries, we can not only mitigate their environmental impact but also contribute to a more resilient and responsible global economy. Through innovation, collaboration, and a shared commitment to sustainability, we can forge a path towards a greener future.
If you recognize the importance of stepping onto this path, let CarbonSWOT be your reliable companion. Get in contact with our ESG experts and develop a tailored approach that would precisely cover your business’ unique necessities.
